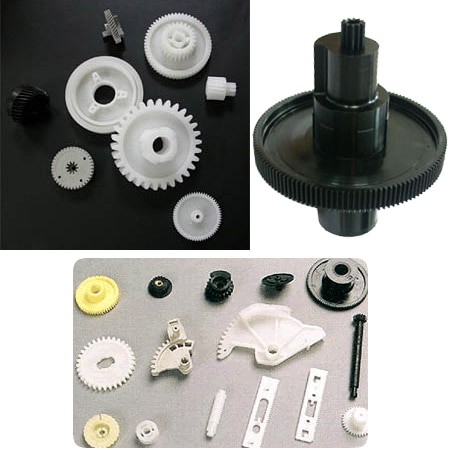
Spur Gear applications


Spur gears are basically cylinders or disks with radially projecting teeth that have straight edges and are aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. The gears are mounted on to parallel shafts so that the teeth can mesh together and transfer motion and power.
Spur gears are the simplest and most common kind of gears and are therefore the first choice in most gear applications.

Spur gears are cost-effective and offer maximum precision; these precision engineered products are easy to manufacture and install. Since the teeth on these gears are parallel to the rotational axis, a spur gear train does not produce axial thrust, making it easy to mount the gear shafts using ball bearings.
In addition, these gears provide a positive, constant speed drive, and unlike belt drives, offer no slip. Spur gears also have high power transmission efficiency (between 95-99%); thus, multiple spur gears may be used to create large gear reductions, and transfer large amounts of power efficiently.
Spur gears mate only one tooth at a time, resulting in noisy operation at high speeds and in high stress on the gear teeth.
The many advantages of spur gears ensure that these gears are used in a wide variety of high speed and high load applications, in all types of gear trains and across a wide range of velocity ratios. They are best suited to multiply the torque, or power, of an object, or to increase/decrease the speed of an object. Hence, spur gears are used in several mechanical applications such as clocks, electric screwdrivers etc., and in many household appliances such as washing machines, blenders, oscillating sprinklers, clothes dryers etc.
Although the loud noise they produce makes them unsuitable for use in car engines, they are used in aircraft engines, and in railway trains, where noise is not an issue. In addition, they are used in slow speed vehicles such as bicycles.
Spur gears are also suitable for high torque-low speed drives such as kilns, ball mills, and sugar mills. ‘Trains’ of spur gears are used in power stations to convert wind or hydroelectric energy into electrical energy.
